How Does PVC Ablation Compare to Other Heart Rhythm Treatments?
- theheartae
- Sep 6, 2025
- 4 min read
Heart rhythm disorders, also known as arrhythmias, affect millions of people worldwide. They occur when the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat do not function properly, causing the heart to beat too quickly, too slowly, or irregularly. One common type of arrhythmia is premature ventricular contractions (PVCs). These are extra heartbeats that originate in the lower chambers of the heart, often described by patients as a "skipped beat" or a sudden thump in the chest.
While occasional PVCs are harmless, frequent or symptomatic ones can disrupt daily life and even increase the risk of more serious heart conditions. Among the different treatment options available today, PVC ablation has emerged as a targeted and effective solution. But how does it compare to other heart rhythm treatments such as medications, lifestyle adjustments, or device implantation? Let’s explore this in detail.
Understanding PVC Ablation
PVC ablation is a minimally invasive procedure performed by an electrophysiologist (a cardiologist specializing in heart rhythm disorders). During the procedure, a thin catheter is guided through the blood vessels into the heart. Using advanced mapping technologies, the doctor pinpoints the exact area in the heart muscle that causes the irregular beats. Once identified, energy (usually radiofrequency heat or sometimes cryotherapy) is applied to destroy the small tissue area responsible for the PVCs, thereby restoring normal rhythm.
PVC ablation is particularly recommended for patients who:
Experience frequent or severe symptoms such as palpitations, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
Do not respond well to medications.
Have PVCs that affect their heart function or lead to cardiomyopathy.
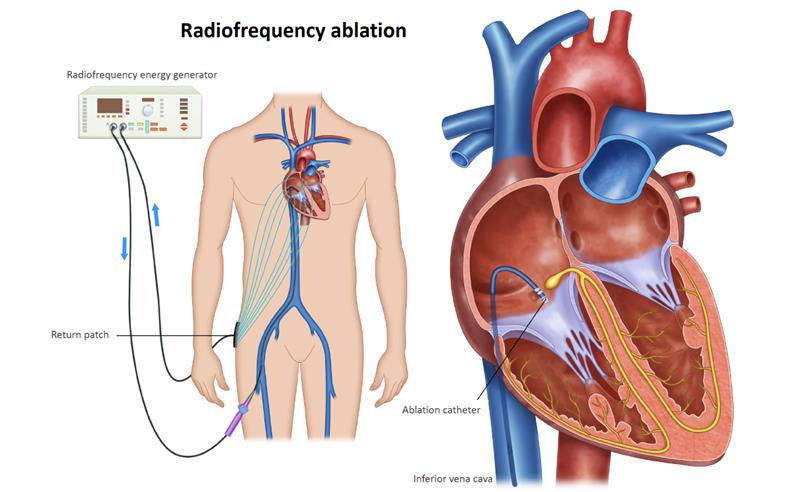
Alternative Heart Rhythm Treatments
While PVC ablation is an advanced option, it is not always the first line of treatment. Let’s compare it to other widely used therapies:
1. Medications
Anti-arrhythmic drugs and beta-blockers are often the first choice for treating PVCs. They help stabilize the heart’s rhythm and reduce the frequency of extra beats.
Advantages:
Non-invasive.
Easily accessible.
Useful in mild cases or when PVCs are triggered by stress, stimulants, or underlying conditions like thyroid imbalance.
Limitations:
Medications may not always fully suppress PVCs.
Some drugs have side effects such as fatigue, dizziness, or low blood pressure.
Long-term dependency may be required, which is not ideal for younger patients.
Compared to medication, PVC ablation offers a more permanent solution, eliminating the source of the arrhythmia rather than just controlling it.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
In certain cases, PVCs are linked to stress, caffeine, alcohol, or poor sleep. Doctors often recommend lifestyle adjustments as a first step.
· Advantages:
· Natural and non-invasive.
· Improves overall cardiovascular health.
· Can reduce the frequency of PVCs in mild cases.
Limitations:
May not be sufficient for patients with persistent or frequent PVCs.
Results can vary from person to person.
While lifestyle changes are always encouraged, they may not eliminate the problem if PVCs stem from a structural or electrical issue in the heart. This is where ablation becomes more relevant.
3. Implantable Devices (Pacemakers or ICDs)
In severe rhythm disorders, patients may require devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs).
Advantages:
Lifesaving in high-risk arrhythmias.
Provide ongoing rhythm regulation and monitoring.
Limitations:
Require surgery and lifelong device management.
Not specifically designed for isolated PVCs unless they are linked to other serious arrhythmias.
Compared to implantable devices, PVC ablation is less invasive, doesn’t involve permanent hardware in the body, and directly targets the problem area.
Comparing Outcomes of PVC Ablation with Other Treatments
Effectiveness:
PVC ablation boasts a high success rate, often above 80–90% in experienced centers, especially when PVCs come from one focal point.
Medications may reduce symptoms but rarely eliminate PVCs entirely.
Lifestyle changes can help, but results are inconsistent.
Safety:
· Ablation is generally safe, though it carries risks such as bleeding, infection, or damage to the heart tissue. However, complications are rare in specialized centers.
· Medications can cause systemic side effects with long-term use.
· Devices involve surgical risks and potential complications over time.
Long-Term Relief:
· Ablation provides durable relief for many patients, often eliminating the need for ongoing drug therapy.
· Medications and lifestyle adjustments usually require continuous adherence.
· Devices provide long-term control but require replacements and follow-ups.
Impact on Quality of Life:
· Ablation can dramatically improve symptoms, energy levels, and emotional well-being for those suffering from frequent PVCs.
· Medications and devices help but often come with ongoing concerns about side effects or dependence.
Is PVC Ablation Always the Best Choice?
While PVC ablation shows excellent outcomes, it is not always necessary. Patients with occasional, harmless PVCs may do well with reassurance, lifestyle modifications, or medications. Ablation becomes the preferred option when:
PVCs significantly impact quality of life.
Medications fail or cause intolerable side effects.
PVCs are linked to declining heart function.
Thus, the choice of treatment must be personalized, guided by the patient’s health, severity of symptoms, and professional evaluation.
The Role of Specialized Centers
Successful outcomes of PVC ablation depend heavily on the expertise of the medical team and the availability of advanced mapping technology. Choosing a trusted provider ensures that patients receive accurate diagnosis, safe procedures, and comprehensive aftercare. In the UAE, The Heartae is recognized for offering advanced cardiac rhythm treatments, including PVC ablation, with specialized care tailored to each patient’s needs.
Conclusion
When comparing PVC ablation to other heart rhythm treatments, it stands out as a highly effective and durable solution for patients with frequent or symptomatic PVCs. Unlike medications or lifestyle changes, which may only provide partial relief, ablation targets the root cause of the problem. While implantable devices play a critical role in managing life-threatening arrhythmias, they are not usually required for isolated PVCs.
Ultimately, the decision between PVC ablation and other treatments should be made in consultation with a cardiac specialist, taking into account the patient’s condition, preferences, and long-term health goals. For those struggling with disruptive PVCs, ablation can offer not only symptom relief but also peace of mind and a better quality of life.



Comments